Wheels come in many different styles, sizes, bolt patterns and offsets. How do we know which wheels will fit a specific vehicle? And further, how can we ensure trouble-free installation?
First, we get to know a vehicle inside and out. Measuring a vehicle's critical components with sophisticated electronic tools allows our fitment engineers to create extremely accurate drawings of these parts. We do the same for wheels, and use Computer Aided Design (CAD) programs to match the wheels to the vehicles. Using these electronic tools, we verify numerous, critical areas before a wheel can be listed as a fit for specific vehicles within our search results.
This attention to detail prevents vibration, wheel/tire interference and unbalanced handling that can result from improperly designed packages.
How Do We Know What Fits?
We scrutinize a dozen major areas before listing any wheel fitments for a vehicle.
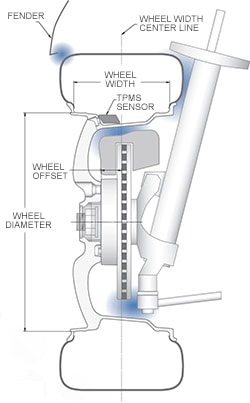
- Wheel Diameter Various measurements are taken to determine applicable wheel diameter options that allow for plus sizing to enhance performance and appearance, as well as minus sizing for some winter tire applications.
- Wheel Width Will the wheel fit within the wheel well? Will there be tires to fit both the wheel width and available clearance on the vehicle?
- Bolt Pattern It's not as simple as 4-lug vs. 5-lug. There are currently over 18 possible patterns ranging in size and spacing from 3 to 8-lug for specific car, CUV, and truck models.
- Centerbore The wheel must, in most cases, fit the hub of the vehicle precisely, either as a direct fit or installed with a centering ring.
- Wheel Offset The wheel offset must allow correct tire clearance and suspension clearance as well as maintain correct suspension and steering geometry.
- Hub Height The height or length of the vehicle hub must be matched to the available depth of the wheel's centerbore area.
- Hub Interference Many vehicles have additional items on the mounting surface area that must be considered for wheel applications, these include locating pins and rotor mounting hardware.
- Brake Profile The shape and size of the brake calipers must fit within the design and shape of the wheel.
- Load Capacity The wheels and tires must have enough load capacity when compared to the gross axle weight rating of the vehicle.
- Lug Hardware The wheel must be securely fastened to the vehicle by either supplying lug hardware or re-using the Original Equipment hardware.
- TPMS Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems are Original Equipment or optional on many of today's vehicles. If the vehicle uses a Direct System with a sensor mounted into the wheel, then the wheel must be produced to accept this sensor.
- Brake and Suspension Components The wheel must clear and not interfere with any of the suspension components and their operation on the vehicle.
The End Result: Easy installation and satisfied customers.